Cathodic Protection Systems: A Comparative Analysis
By Joe Pikas

Cathodic Protection (CP) systems are critical in safeguarding pipelines against corrosion, which can lead to costly failures and environmental harm. Let’s evaluate the different types of CP systems, comparing their materials, technologies, installation processes, and cost-efficiency while discussing the latest advancements.
Understanding Cathodic Protection Systems
Cathodic Protection systems work by reducing the corrosion potential of a metal surface. By applying a small electric current, they ensure the structure (pipeline, tank, etc.) becomes the cathode in an electrochemical cell, preventing corrosion. Two primary types of CP systems exist: galvanic (sacrificial anode) and impressed current systems (ICS).
Comparing Cathodic Protection Systems
-
Materials: Anode vs. Cathode
-
- In galvanic CP, sacrificial anodes such as magnesium or zinc degrade over time, protecting the pipeline. Impressed current systems use inert anodes like graphite, mixed metal oxide (MMO) that require an external power source but last longer. The choice between these depends on soil resistivity and lifecycle cost analysis.
-
Installation Comparisons
-
- Galvanic Systems: Easier and quicker to install, often used for localized protection
- Impressed Current Systems: More complex but suitable for large-scale pipelines and structures, offering extensive coverage
-
Cost-Benefit Analysis
-
- While galvanic systems are less expensive upfront, ICS systems often provide a better long- term cost-efficiency for large-scale projects due to their durability and lower replacement frequency.
Evaluating CP System Performance
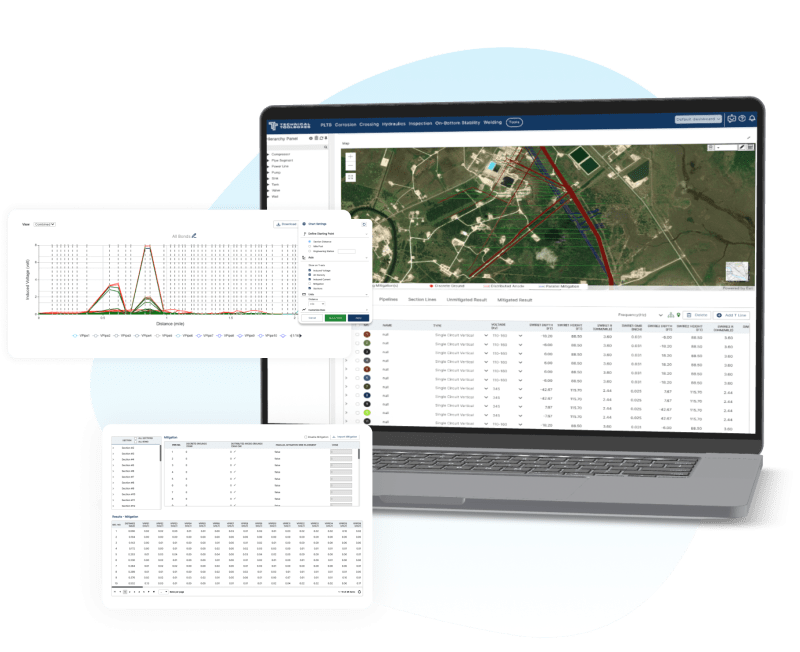
The performance of CP systems depends on several factors, including soil resistivity, pipeline material, and coating quality. Tools like the Technical Toolboxes’ Pipeline Toolbox (PLTB) streamline CP system design by automating calculations for current and anode requirements.
Key Metrics
- Anode Output Efficiency: Determines how effectively the system provides protection.
- System Attenuation: Advanced tools like the AC Mitigation PowerTool (ACPT) help evaluate the impact of AC-induced corrosion, crucial for pipelines near power lines.
- Power Consumption: ICS systems often require rectifiers. Advanced rectifiers, analyzed in the Pipeline HUB, offer precise power control, reducing operational costs.
Latest Technologies in Cathodic Protection
- AC Mitigation and Modeling
-
- The AC Mitigation PowerTool enables engineers to model pipelines near power lines, identifying potential risks and optimizing mitigation strategies through GIS integration.
- Integration with Pipeline HUB
-
- Centralized platforms like the Pipeline HUB offer GIS visualization, reporting, and automated data synchronization, enhancing CP project planning and execution.
- Advanced Calculations
-
- Tools like Batch Run and Sensitivity Analysis facilitate rapid testing of multiple CP scenarios, ensuring optimal system design.
CP System Selection Criteria
When selecting a CP system, consider:
- Structure Current Requirements: ICS for larger systems, galvanic for smaller systems
- Soil Resistivity: High-resistivity soils require ICS
- Regulatory Compliance: Engineering Tools like the Pipeline Toolbox ensure adherence to standards like PHMSA, PRCI, AMPP, ASME, API, etc.
Conclusion
Cathodic Protection is an indispensable tool in pipeline integrity management. By leveraging advanced technologies like the Pipeline Toolbox and AC Mitigation PowerTool, operators can enhance CP system performance while optimizing costs. As CP technologies evolve, the focus on efficiency, integration, and compliance continues to drive industry innovation.
Have questions about CP systems? Let us guide you through the latest tools and best practices for your pipeline projects.
Suggested Post
The Network Modeling Tool Gas Engineers Didn’t Know They Needed
The Network Modeling Tool Gas Engineers Didn’t Know They Needed By Kesley Price You’ve outgrown your spreadsheets, now [...]
The Trusted Tool Gas Engineers Didn’t Know They Were Missing
Do You Really Know What’s Flowing Through Your Pipes? The Trusted Tool Gas Engineers [...]
2026 API Compliance: What You Need to Know
2026 API Compliance: What You Need to Know By Kesley Price New rules. Tougher [...]











