Analyzing Corrosion and Remaining Strength of Pipes
By Amirali Panjwani

Introduction
Pipeline operators constantly encounter regulatory restrictions and economic obstacles to maintain exceptional standards of quality, productivity, and compliance. An issue that persistently presents a threat to these standards is corrosion of the pipeline. To address this issue of maintaining pipeline integrity, pipeline engineers require a computational solution that can determine the remaining strength of pipes and effectively manage the assessment cycle of multiple assets.
Combating Corrosion Strategically
In today’s competitive market, effectively combating corrosion requires a strategic asset management plan that strikes a balance between safe operations and budget limitations. As corrosion progresses, the pipe wall gradually loses more metal, potentially leading to leaks or ruptures in thin areas. The conservative approach of repairing or replacing pipes when in doubt can result in a costly list of repair projects. However, reducing this conservatism while ensuring pipeline integrity calls for investing in tools that minimize uncertainty. Although it may require increased spending initially, these investments ultimately offset larger expenditures associated with repairs.
Challenges of Selecting a Corrosion Analysis Software
With the range of options available today, it can be challenging to determine the varying levels of value offered by each option. The following are some key factors to take into consideration when making a selection: 
Managing Cost:
- Conducting inspections by digging up pipelines incurs significant costs.
- A single excavation for inspection purposes can start at a baseline of fifty thousand dollars, and in densely populated urban areas, these costs can quickly escalate into millions of dollars.
- Investigative digs are inherently expensive, and so are the subsequent repairs and failures that may arise.
- Additionally, audit findings and the time spent by pipeline engineers add to the overall expenses.
To mitigate these costs, it is crucial to have the right tool that can streamline the engineering analysis process and ensure safe operations. A flexible tool that can meet these requirements effectively reminds the user about the proper handling of exceptions, thereby reducing the number of engineering analysis hours required.
Reducing Risk
While the focus is often on minimizing the risk of leaks and ruptures, it is important to recognize that there are inherent risks associated with various processes that support and enable corrosion analysis. An ideal solution should not only assess the risk posed by existing corrosion but also help mitigate risks in other areas of the business. When considering software purchases, a key decision factor should be the ability of the solution to optimize and prioritize schedules in order to reduce risks across multiple aspects of corrosion management. This holistic approach ensures that all facets of the business are considered, leading to more effective risk reduction strategies.
Adhering to Regulations
The emergence of new regulations and rules is an ongoing process, often prompted by significant events and incidents such as spills or ruptures. When confronted with demands for inspections by regulators, it is imperative to have a remaining strength solution that can provide accurate corrosion assessments and comprehensive audit reporting. Such a solution ensures compliance with regulatory requirements and enables thorough evaluation of pipeline integrity by delivering reliable results and detailed reports.
RSTRENG+ as a Solution
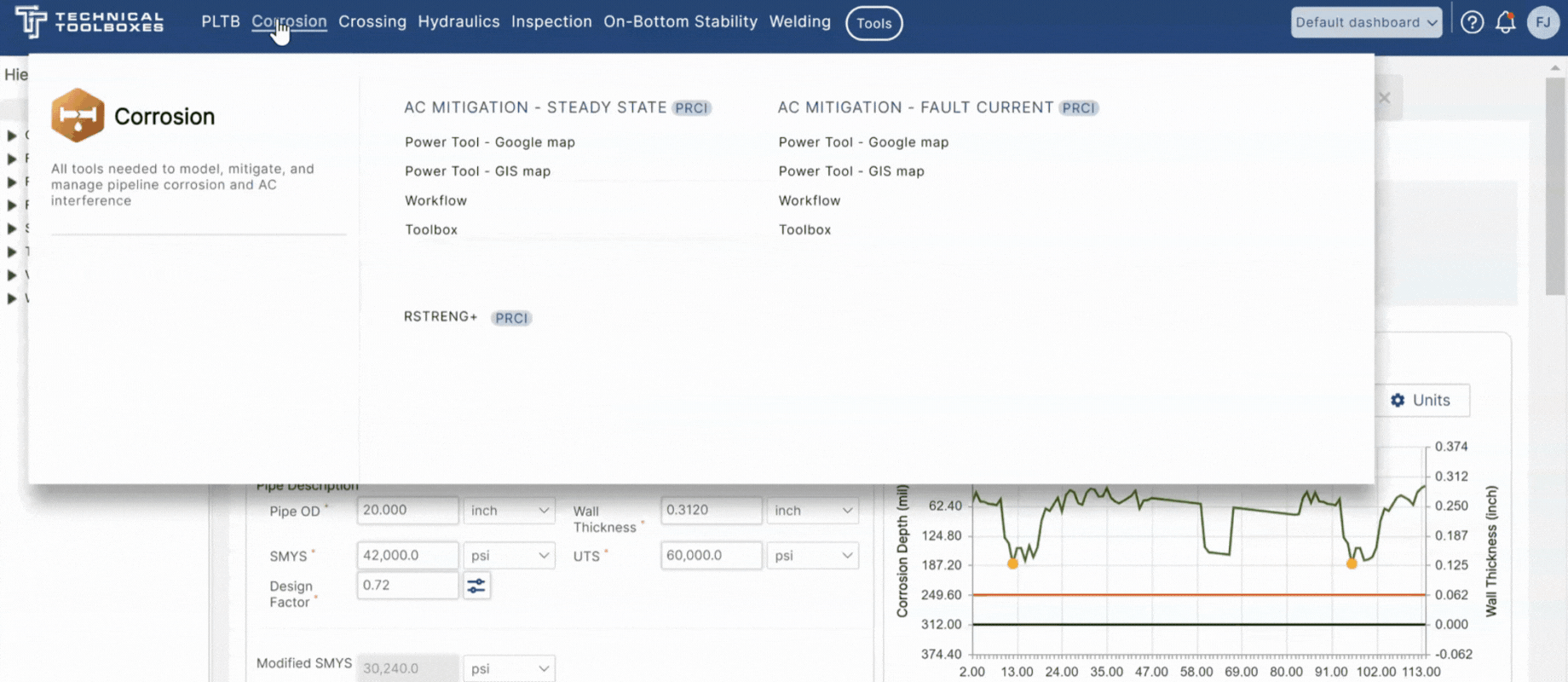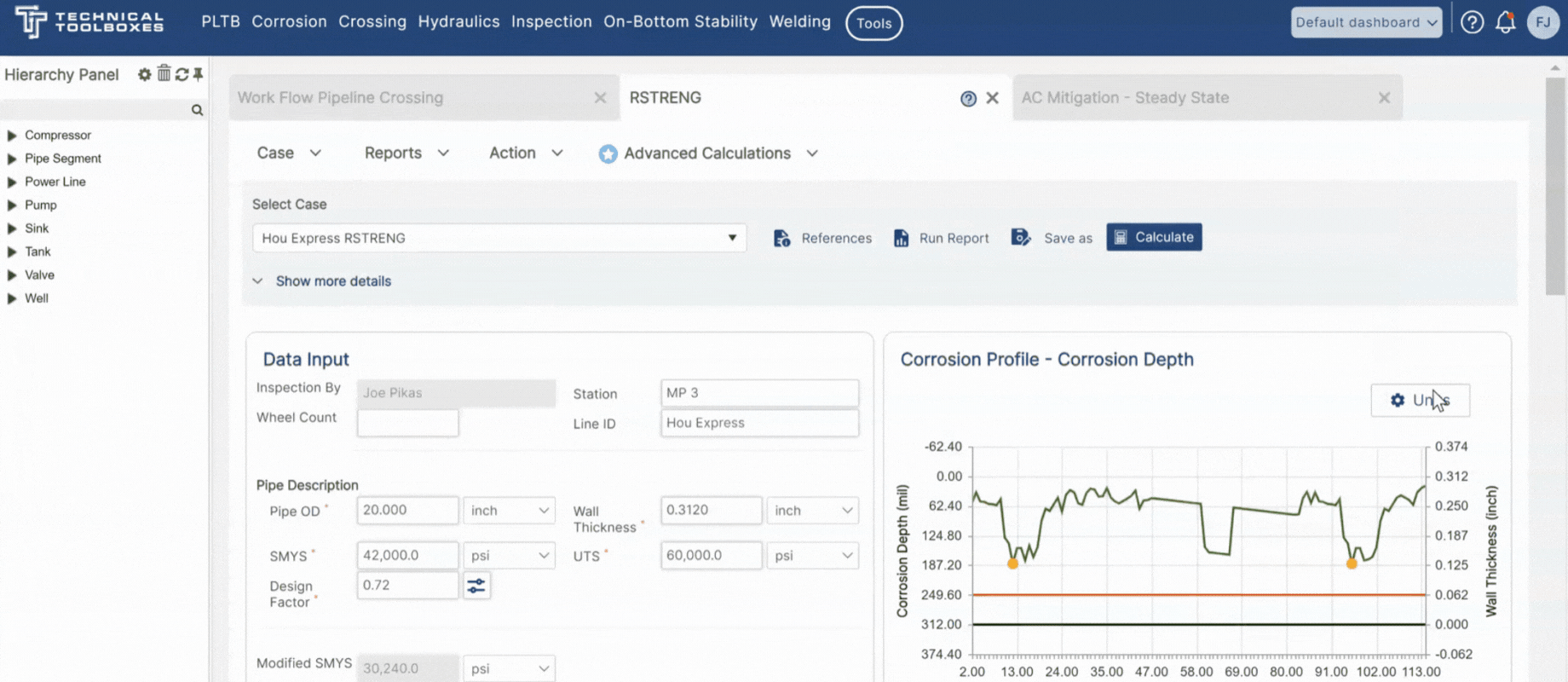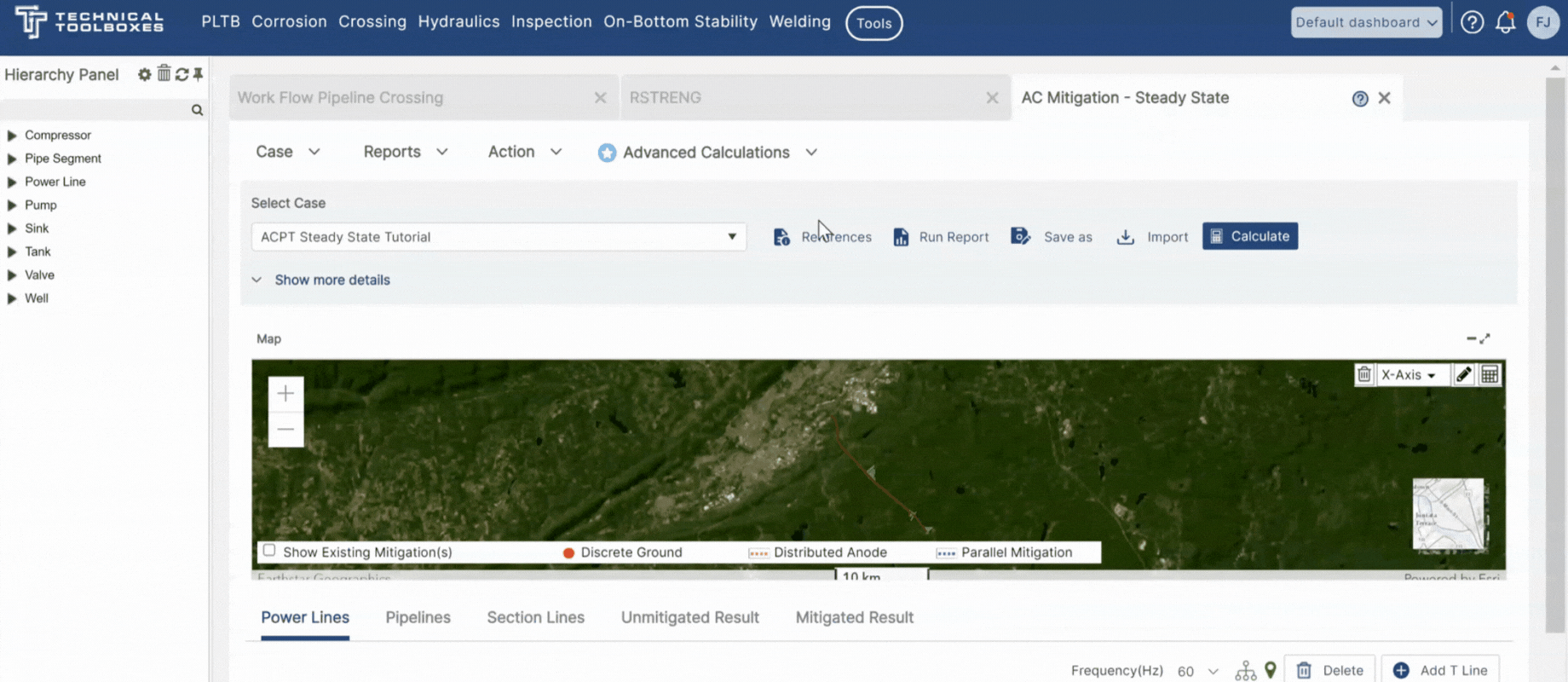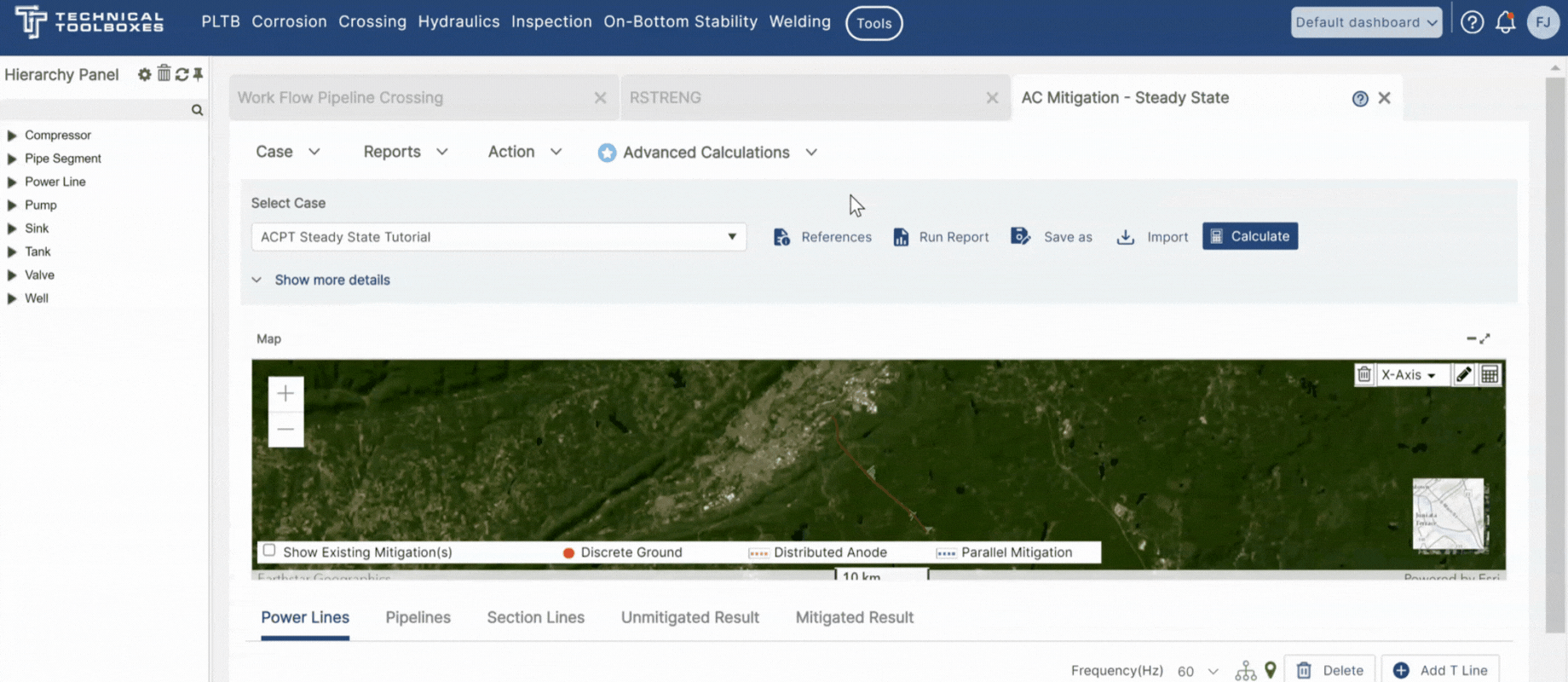
Technical Toolboxes RSTRENG+ software provides an extensive solution combining the PRCI-backed RSTRENG software with multiple advanced features and calculations that facilitate better integrity repair decisions reducing risk and improving the quality of engineering operations. RSTRENG+ is built on top of the RSTRENG engine, which is the only Level 2 methodology sanctioned by the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) to calculate remaining strength along extended lengths of pipe. The automatic workflows of RSTRENG+ drastically reduce the manual work while concurrently increasing the speed, accuracy, and confidence, with which an engineer can complete integrity analysis projects.
Features of RSTRENG+
RSTRENG+ comes equipped with advanced features such as Batch Run and the Zero-Out Method along with Non PRCI calculations to accommodate multiple scenarios and the traceable, verifiable, complete (TVC) recordkeeping to comply with the Mega Rule under the Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration (PHMSA).
- Zero-Out Method – gives engineers the ability to pinpoint effective areas of corrosion along a pipeline that need repair, within miles of inspection data, to operate at the desired Maximum Allowable Operating Pressure (MAOP).
- Non PRCI Calculations – offers reassessment interval calculation to reduce risk and cost through optimizing the number of times a pipe is assessed while balancing integrity needs in resource-constrained environments. It also includes remaining strength calculations (SHELL-92, DNV, PCORRC, API579) that provide flexibility to accommodate different scenarios along with facilitating knowledge transfer.
- Batch Run – an advanced Pipeline HUB platform feature allowing users to simulate multiple case runs in a single execution. Users can execute cases against pre-defined model validation limits and be provided with an execution summary. Executions summaries created through this feature can aid with the record keeping for future TVC compliance.
RSTRENG+ is the ideal solution to support calculations and business processes throughout the life of a pipe. Using the RSTRENG+ can greatly reduce the cost for pipeline maintenance with the multiple levels of repair options available, along with the ability to verify and avoid costly, catastrophic failure events through the identification of multiple metal loss defects.
Conclusion
For more information regarding this blog topic, please join us for our training on “Corrosion Management of Aging Pipelines“.

The Network Modeling Tool Gas Engineers Didn’t Know They Needed
The Network Modeling Tool Gas Engineers Didn’t Know They Needed By Kesley Price You’ve outgrown your spreadsheets, now [...]
The Trusted Tool Gas Engineers Didn’t Know They Were Missing
Do You Really Know What’s Flowing Through Your Pipes? The Trusted Tool Gas Engineers [...]
2026 API Compliance: What You Need to Know
2026 API Compliance: What You Need to Know By Kesley Price New rules. Tougher [...]