Mastering Pipeline Calculations: From ASTM Standards to ASME B31.3
By Kesley Price

Pipeline engineering involves a complex array of calculations and standards designed to ensure the safety, reliability, and efficiency of pipeline systems. Two essential organizations that provide widely used standards are ASTM International and the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME). Engineers working on pipeline design, construction, and maintenance often rely on ASTM standards for pipelines and ASME B31.3 calculations to ensure compliance with industry norms and regulatory requirements. This blog will explore how mastering these standards can enhance pipeline engineering calculations, mitigate risks, and improve operational outcomes.
Understanding ASTM Standards for Pipelines
ASTM International plays a critical role in developing standards that address various aspects of pipeline materials, including properties like viscosity, temperature relations, and material strength. One crucial ASTM standard used in pipeline engineering is ASTM D341, which covers the viscosity-temperature relations for hydrocarbons. This standard provides the framework for calculating fluid viscosity changes due to temperature variations, a key factor in determining flow rates, pipeline pressure, and overall system performance.
For more details, visit ASTM D341 – Viscosity-Temperature Relations for Hydrocarbons.
ASME B31.3 and Its Importance in Pipeline Design
On the other hand, ASME B31.3 sets the groundwork for process piping systems and has become the go-to code for pipeline engineers working in critical applications such as oil, gas, and chemical transport. This standard outlines the design, material selection, construction, and inspection criteria necessary to ensure pipeline integrity, especially in high-pressure environments.
Key calculations included in ASME B31.3 focus on pipe stress analysis, wall thickness design, and corrosion allowances. Using these calculations ensures that the system can handle internal and external pipeline pressure forces while minimizing the risk of failure. Additionally, engineers must be adept at validating welded branch connections for strength and integrity under ASME B31.8 and B31G guidelines, particularly for natural gas pipelines.
For more details on branch connection validation, visit Validation Check for Reinforcement of Welded Branch Connections.
Mastering Pipeline Engineering Calculations with Advanced Tools
Gone are the days when engineers relied solely on spreadsheets for complex pipeline calculations. Tools like the Pipeline Toolbox (PLTB) offer a comprehensive suite of over 250 industry-standard pipeline calculations, simplifying the process while ensuring compliance with ASTM and ASME standards.
PLTB includes modules for pipeline crossings, stress analysis, hydraulics, and corrosion management—essential for adhering to standards such as ASME B31.3. The software eliminates the need for manual data entry, significantly reducing errors and streamlining workflows for engineering teams.
To explore the benefits of the Pipeline Toolbox, visit Pipeline Toolbox (PLTB).
ASME and ASTM in Pipeline Design: A Combined Approach
Pipeline engineers are often tasked with designing systems that must adhere to both ASTM and ASME standards. For instance, when calculating the Maximum Allowable Operating Pressure (MAOP) of a pipeline, both material properties (governed by ASTM standards) and pipeline stress analyses (guided by ASME B31.3) play integral roles. Misalignment between these two standards can result in costly rework or even pipeline failure.
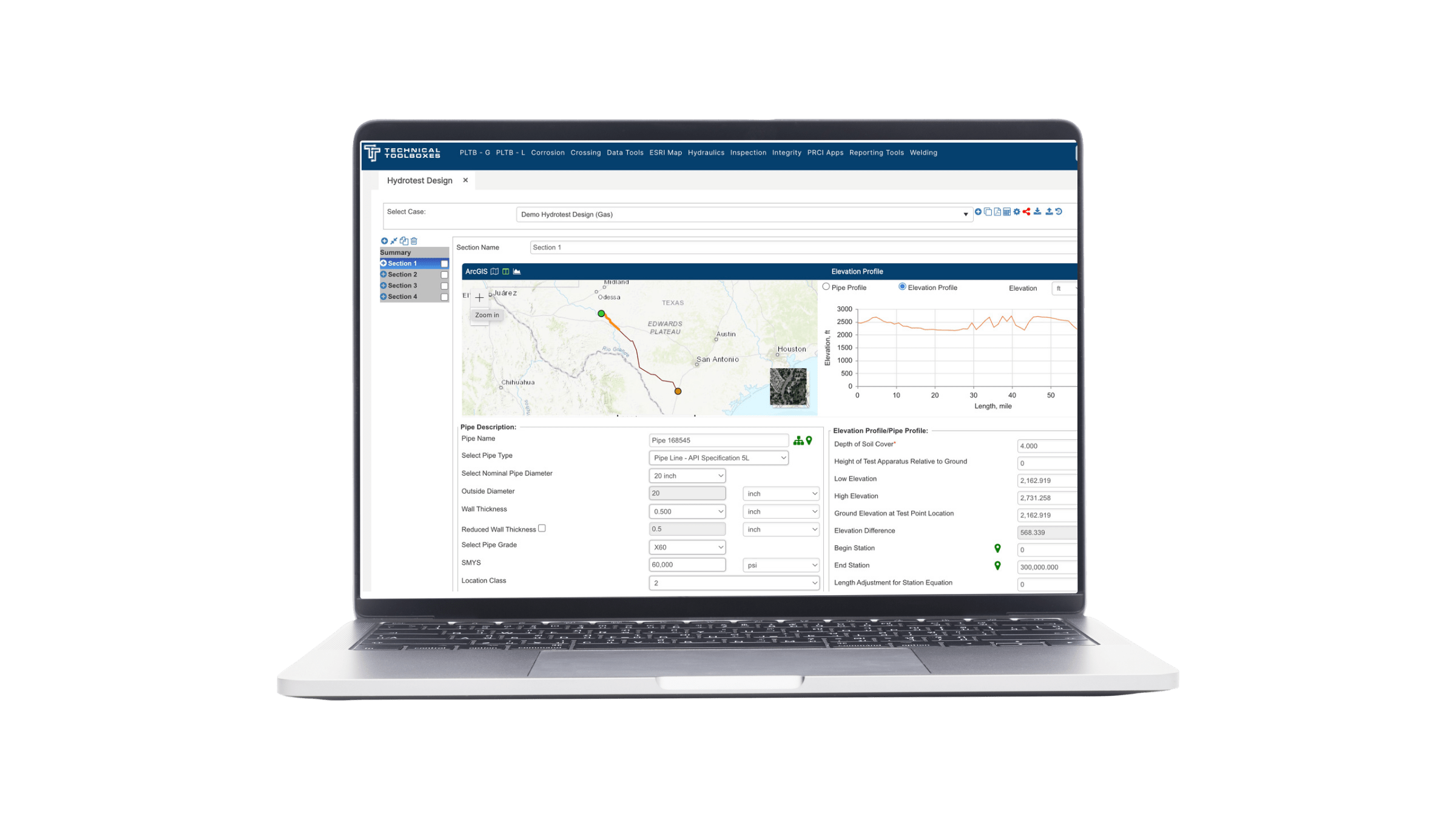
Hydrotest PowerTool
A robust approach to mastering these calculations involves using automated tools like Hydrotest PowerTool and RSTRENG+, which can handle simultaneous calculations, cross-reference multiple standards, and offer precise diagnostics for pipeline strength. The Hydrotest PowerTool is invaluable for validating pipeline integrity during construction and operational phases by verifying the MAOP according to CFR 192 and 195 regulations.
For more information on MAOP verification, visit Hydrotest PowerTool Overview.
Conclusion: Enhancing Pipeline Engineering Through Standards
Mastering ASTM standards for pipelines and ASME B31.3 calculations is critical for pipeline engineers aiming to enhance system safety and efficiency. By incorporating tools like Pipeline Toolbox and Hydrotest PowerTool, engineering teams can streamline complex calculations, minimize human error, and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
As the industry advances, leveraging these tools and standards will remain crucial in mitigating risks and improving the operational longevity of pipeline systems. Engineers who continuously refine their expertise in ASTM and ASME standards will be well-positioned to navigate the evolving challenges in pipeline design, construction, and integrity management.
Suggested Post
The Network Modeling Tool Gas Engineers Didn’t Know They Needed
The Network Modeling Tool Gas Engineers Didn’t Know They Needed By Kesley Price You’ve outgrown your spreadsheets, now [...]
The Trusted Tool Gas Engineers Didn’t Know They Were Missing
Do You Really Know What’s Flowing Through Your Pipes? The Trusted Tool Gas Engineers [...]
2026 API Compliance: What You Need to Know
2026 API Compliance: What You Need to Know By Kesley Price New rules. Tougher [...]












