Decoding AC Interference in Pipeline Operations
By Kesley Price

Alternating Current (AC) interference is a significant concern for buried pipelines, particularly when they are in proximity to high-voltage power lines. This blog explores the intricacies of AC interference, focusing on the electromagnetic (inductive) coupling, which is the dominant mechanism affecting pipelines under normal power line conditions.
Electromagnetic (Inductive) Coupling
Inductive coupling occurs when an electromagnetic field generated by an AC power line induces a voltage in a nearby pipeline. This interaction is primarily influenced by current flow rather than voltage, the balance of the circuit, and the spatial relationship between the power line conductors and the pipeline. Factors such as the distance between conductors, their mutual impedance, and the presence of passive conductors (like shield wires or other metallic structures) significantly affect the level of induced voltage.
Modeling and Analysis of Induced AC Voltages
The transmission line model offers a structured approach to estimate induced voltages in pipelines. This model incorporates the longitudinal electrical field (LEF), a crucial factor in understanding the extent of AC interference. The LEF is affected by various elements, including:
- The current in the high-voltage power line (HVPL).
- The mutual impedance between the pipeline and HVPL.
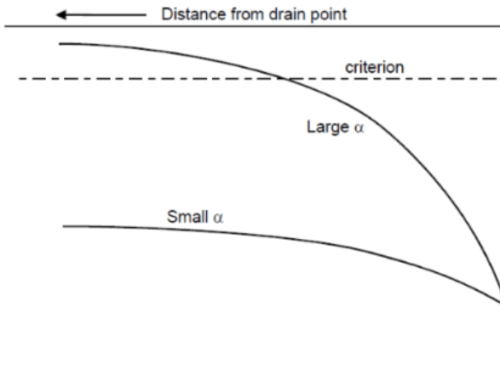
The model distinguishes between electrically short and long pipelines, providing insights into how induced voltages are distributed along the pipeline’s length.
AC Interference Threats and Mitigation
AC interference poses risks, especially in locations where the physical geometry between the power line and pipeline changes, such as at crossings or where they diverge. The voltage peaks at these points can significantly impact pipeline integrity. Mitigation strategies, like grounding, are essential to manage these induced voltages effectively. However, grounding must be applied judiciously to avoid exacerbating the interference issues.
The Role of AC Mitigation PowerTool (ACPT) 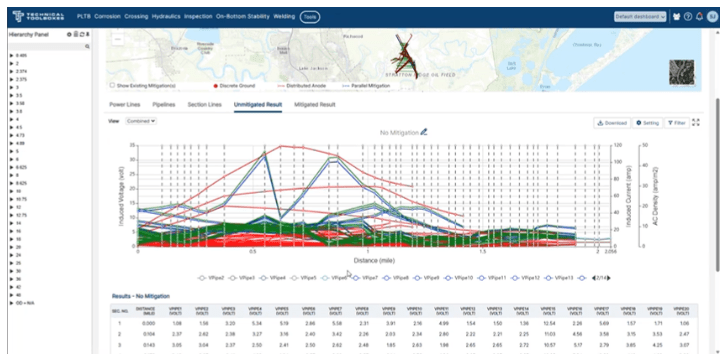
Technical Toolboxes’ AC Mitigation PowerTool (ACPT) is a comprehensive solution for analyzing, modeling, and mitigating AC interference effects on pipelines. ACPT assists in detailed analysis by considering various factors like:
- Soil resistivity.
- Pipeline coating stress.
- Positioning of power lines relative to pipelines.
Conclusion
Understanding and mitigating AC interference in pipelines is crucial for maintaining their integrity and operational safety. Through advanced modeling and analytical tools like ACPT, engineers can effectively manage the complexities of AC interference, ensuring the long-term reliability of pipeline infrastructure.
Understanding and mitigating AC interference is vital for the integrity and safety of pipeline operations. Advanced modeling and analysis tools, like the AC Mitigation PowerTool, equip engineers with the necessary resources to address the challenges posed by electromagnetic interference. These tools enable a comprehensive approach to AC interference, ensuring reliable and efficient management of pipeline infrastructure in the face of complex environmental and operational conditions.
Suggested Post
The Network Modeling Tool Gas Engineers Didn’t Know They Needed
The Network Modeling Tool Gas Engineers Didn’t Know They Needed By Kesley Price You’ve outgrown your spreadsheets, now [...]
The Trusted Tool Gas Engineers Didn’t Know They Were Missing
Do You Really Know What’s Flowing Through Your Pipes? The Trusted Tool Gas Engineers [...]
2026 API Compliance: What You Need to Know
2026 API Compliance: What You Need to Know By Kesley Price New rules. Tougher [...]