Introducing PRCI Thermal Analysis Version 5
By Amir Panjwani
Introduction
Technical Toolboxes is excited to share some thrilling news with you: the Pipeline Research Council International (PRCI) community has dedicated 20 years to meticulous research, and as a result, Technical Toolboxes is proud to unveil the latest version of the PRCI Thermal Analysis Software, also known as Hot Tap. Throughout these last two decades, numerous advancements have taken place, but one this has always remained unchanged: the crucial requirement for precise calculations.
For pipeline operators and engineers, maintaining confidence in their results is a constant challenge. One of the main culprits behind this uncertainty is the reliance on spreadsheets for analysis. Unfortunately, using spreadsheets can lead to inaccurate and unreliable results, compromised data security, and non-compliance with industry standards. Moreover, the risk of error increases potentially jeopardizing safety and incurring additional operational and capital expenses. With the introduction of PRCI Thermal Analysis Version 5, the risk of errors is significantly reduced, allowing you to regain the confidence in your results that should have been present from the very beginning.
What’s New in Version 5
The advancements made in PRCI Thermal Analysis Version 5 are as follows:
1. Predicting measurement of heat sink has been improved
Rapid cooling after welding poses a significant risk of hydrogen cracking in pipelines, as the flowing contents swiftly remove heat. To prevent this issue, higher levels of heat are necessary for the weld. With the latest version, PRCI has made significant enhancements to the calculations, surpassing the capabilities of the previous version. Through multiple experimental iterations, the calculations have become more precise and resilient, ensuring the pipe can safely withstand the required amount of heat, provided the fundamental procedure is followed, enabling a more accurate determination of heat capacity, further enhancing the overall reliability of the calculations.
2. Enhancement for assessment of attachments
When determining the heat sink capacity for in-service pipes, it is important to not only consider the pipes themselves but also any attachments, such as hot-formed fittings, which can have less favorable chemical compositions i.e., higher carbon-equivalent level, and may pose a greater risk of cracking compared to the pipe material. The latest version introduces the ability to predict the hardness factor in the heat-affected zone (HAZ) for both the pipe and the attachment. This advancement enables the calculations of heat capacity for both the attachment and the pipe, resulting in enhanced accuracy and usability in real-world applications.
3. New Microstructure model integrated with the thermal model
A sophisticated microstructure model has been developed in this latest version to analyze the impact of various microstructure components (bainite, martensite, pearlite, and ferrite) and the cooling rate on the HAZ. By leveraging the inherent properties of the microstructures, simulations are conducted by the software to accurately determine the final HAZ hardness and prevent pipe cracking.
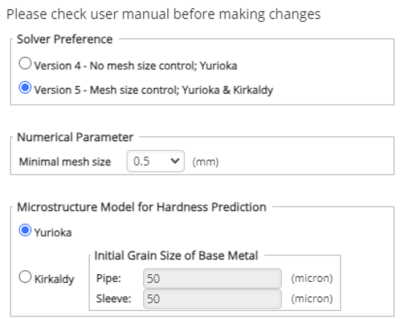
4. Improved mesh generator
Mesh generation involves dividing a geometric shape into smaller subdivisions, known as mesh, to approximate the larger area. The current version of PRCI Thermal Analysis, only provides a fixed mesh control size according to the Yurioka method, limiting the flexibility and precision of calculations. Excitingly, Version 5 introduces an alternate, the Kirkaldy method, that enables the users to modify mesh size and parameters, offering enhanced accuracy in calculations.
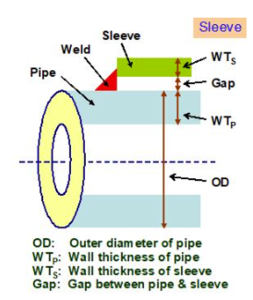
5. Schematics for visual representation
Graphics are now available in this new version as descriptive depictions of the various geometries of sleeves, branches, and beads on pipes. These drawings serve as valuable aids for user of the software, regardless of their level of expertise, significantly reducing the time required for onboarding and training. By offering a visual understanding of the selected geometries, the software streamlines the learning process, enabling users to quickly grasp the concepts and effectively utilize the software’s capabilities.
Conclusion
Technical Toolboxes strives to deliver optimal solutions for pipeline integrity analysis, always aiming to meet the needs of the pipeline engineering community. The recent launch of the latest version of PRCI Thermal Analysis Software marks another significant milestone in our commitment to innovation.
As the rules and regulations governing pipeline integrity progress, our solutions will continue to evolve to keep pace with these advancements.

The Network Modeling Tool Gas Engineers Didn’t Know They Needed
The Network Modeling Tool Gas Engineers Didn’t Know They Needed By Kesley Price You’ve outgrown your spreadsheets, now [...]
The Trusted Tool Gas Engineers Didn’t Know They Were Missing
Do You Really Know What’s Flowing Through Your Pipes? The Trusted Tool Gas Engineers [...]
2026 API Compliance: What You Need to Know
2026 API Compliance: What You Need to Know By Kesley Price New rules. Tougher [...]










