Understanding On-Bottom Stability in Pipeline Design
By Kesley Price
Ensuring the stability of subsea pipelines is a fundamental aspect of pipeline design that cannot be overlooked. On-bottom stability, the ability of a pipeline to remain stable on the seabed amidst various environmental forces, plays a crucial role in maintaining the pipeline’s integrity and functionality. In this blog, we will explore the key components of on-bottom stability for pipelines, including hydrodynamic forces, soil-pipeline interaction, and the methods used for stability analysis.
What is On-Bottom Stability?
On-bottom stability refers to the capability of a subsea pipeline to stay securely positioned on the seabed without excessive movement or displacement due to environmental conditions. Achieving this stability is essential to prevent pipeline damage, ensure uninterrupted operation, and reduce maintenance costs.
Hydrodynamic Forces on Pipelines
Hydrodynamic forces, such as those exerted by waves and currents, are significant challenges to maintaining on-bottom stability. These forces can cause oscillatory motions in the pipeline, leading to fatigue and potential failure if not properly managed. Accurate modeling of these forces is vital for designing stable pipelines.
Soil-Pipeline Interaction 
The interaction between the pipeline and the seabed soil is another crucial factor in on-bottom stability. Different soil types, including clay, sand, and silt, provide varying levels of resistance against hydrodynamic forces. Understanding these interactions helps engineers design pipelines that can withstand environmental stresses effectively.
Subsea Pipeline Stability Criteria
Stability criteria for subsea pipelines are determined based on several factors, including the pipeline’s weight, diameter, and the type of seabed soil. Engineers adhere to various design codes and standards, such as the DNVGL-ST-F101 standard, which outlines the stability requirements for submarine pipeline systems.
Calculating On-Bottom Stability
Calculating on-bottom stability involves several steps:
- Assessment of Environmental Conditions: Analyzing wave and current patterns in the pipeline’s location.
- Soil Analysis: Evaluating the type and properties of the seabed soil.
- Pipeline Characteristics: Considering the pipeline’s diameter, weight, and coating.
- Stability Analysis: Utilizing mathematical models and simulations to predict the pipeline’s behavior under different conditions.
Stability Analysis in Pipeline Engineering
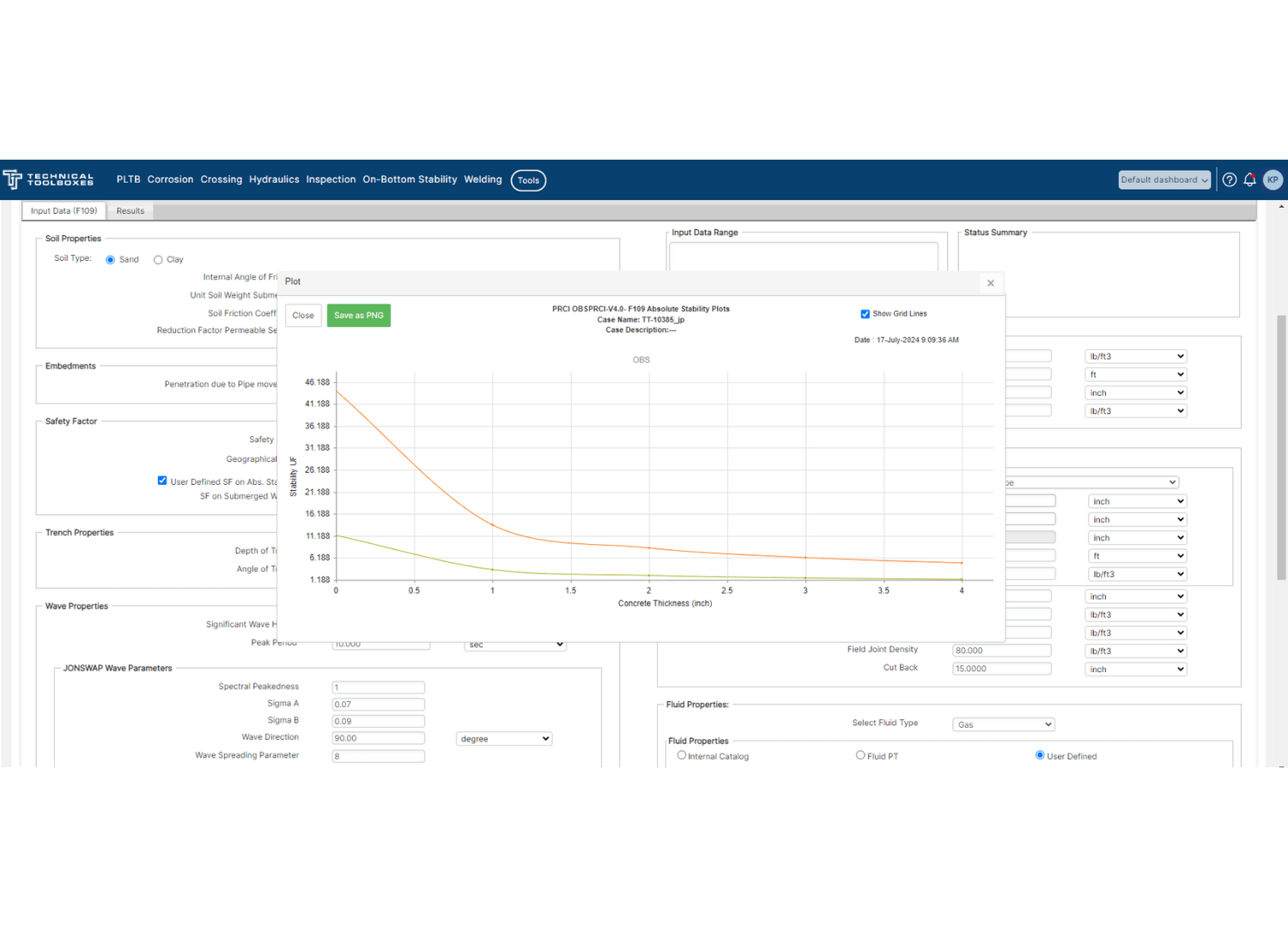
Stability analysis employs specialized software tools to simulate the pipeline’s behavior under various scenarios. These tools model the impacts of hydrodynamic forces and soil interactions, enabling engineers to design pipelines that meet stability requirements. Technical Toolboxes’ On-Bottom Stability (OBS) software, developed together with the Pipeline Research Council International (PRCI), is a powerful tool for performing these analyses efficiently and accurately.
Technical Toolboxes’ OBS Software
At Technical Toolboxes, we offer advanced solutions like the On-Bottom Stability (OBS) software, which aids in the accurate analysis and simulation of pipeline stability. Our OBS software helps engineers design robust and reliable subsea pipelines, ensuring they meet all necessary stability criteria. By leveraging our software, you can optimize your pipeline projects and mitigate risks associated with on-bottom stability.
Conclusion
On-bottom stability is a crucial aspect of pipeline design that ensures the safety and functionality of subsea pipelines. By understanding and managing hydrodynamic forces, soil-pipeline interactions, and conducting thorough stability analyses, engineers can design pipelines that are both robust and reliable.
For more detailed insights and advanced tools for on-bottom stability analysis, visit Technical Toolboxes.
Suggested Post
The Network Modeling Tool Gas Engineers Didn’t Know They Needed
The Network Modeling Tool Gas Engineers Didn’t Know They Needed By Kesley Price You’ve outgrown your spreadsheets, now [...]
The Trusted Tool Gas Engineers Didn’t Know They Were Missing
Do You Really Know What’s Flowing Through Your Pipes? The Trusted Tool Gas Engineers [...]
2026 API Compliance: What You Need to Know
2026 API Compliance: What You Need to Know By Kesley Price New rules. Tougher [...]