PHMSA Mega Rule Compliance Using Software
By Joe Pikas

Introduction to Rulemaking for Pipeline Safety
The first set of prescriptive regulations designed to improve safety by reducing the frequency of pipeline failures was brought about by the Gas Rule in 1971. This original rulemaking was the result of the many failures pipeline operators were experiencing at the time. Multiple rules after that were set into place to ensure compliance with safety standards.
In 2003, the Integrity Rule was introduced, which was a comprehensive, systematic, and fully integrated integrity management program. An integrity management program provides the information for an operator to effectively allocate resources for appropriate prevention, detection, and mitigation activities resulting in improved safety and a reduction in the number of incidents
Creation of the PHMSA Mega Rule
These rules go relatively unchanged as pipeline failures are largely uncommon, but an occurrence can both be devastating and costly for the local population and the environment. Occurrences such as the San Bruno pipeline explosion in 2010 served as the tipping point for perhaps the largest update in public policy in the oil and gas sector to be seen in years. A decade in the making, The Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration (PHMSA) released a rule so massive that it has been dubbed the “Mega Rule.” Due to its size, the rule is divided into three parts:
- Part 1 (2020) Focused on Material Verification (MAOP), Expansion of Assessments, and TVC
- Part 2 (2022) Corrosion, Excavation Damage (Encroachment), Construction, Repair Criteria from Integrity Activities
- Part 3 (2023) Jurisdiction of Type C Onshore Gathering Lines (426,000 miles)

Preparing for Implementation
The Mega Rule is so comprehensive that a compliance deadline has been set for 2035, more than a decade into the future. However, Technical Toolboxes has been planning for the Mega Rule’s significant changes for integrity, operating, and compliance needs of pipeline operators. The focus will consist of digitizing, mapping, and streamlining the integration of all data to meet the traceable, verifiable, complete (TVC) regulatory requirements.
Solutions for Regulatory Compliance
The Technical Toolboxes’ Pipeline HUB serves as an all-in-one platform to manage all data in compliance with the increased reporting and safety regulations of part 1 of the Mega Rule. The ability to configure asset data once and plug it into any application on the Pipeline HUB minimizes the risk of errors and automates the PHMSA compliance reporting process for pipelines. Alongside the Pipeline HUB, the Pipeline Toolbox Gas Version (PLTBG) consists of many applications such as Pipeline Crossings Cathodic Protection and Design and Stress Analysis that assist in external corrosion control (192.463) and continued surveillance (192.613) in accordance with the PHMSA regulations.
Webinar on PHMSA Mega Rule Compliance
For a more detailed discussion on PHMSA Mega Rule compliance and how to effectively use software solutions for implementation, you can view our previously recorded webinar presented by Joe Pikas, an expert in pipeline safety and integrity. This webinar provides in-depth insights and practical examples to help pipeline operators navigate the complexities of the Mega Rule.
Conclusion
See below for a full list of solutions offered by Technical Toolboxes to assist in regulatory compliance with the PHMSA Mega Rule for oil and gas pipelines, improving pipeline projects management and reporting. Click here to speak to an engineering advisor or request a demo for one of our suites.
PHMSA Mega Rule Solutions
| Product | Features | PHMSA Rule Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| Pipeline HUB | Configure data once & plug it into any application Reduce time spent on data mining & entry Minimize calculation errors & risk Automate reporting with the click of a button Visually depict pipeline assets using ArcGIS |
192.917, 192.607 |
| Pipeline Toolbox (PLTB) | Pipeline Crossing Cathodic Protection Pipeline Design & Stress Analysis |
192.613, 192.463 |
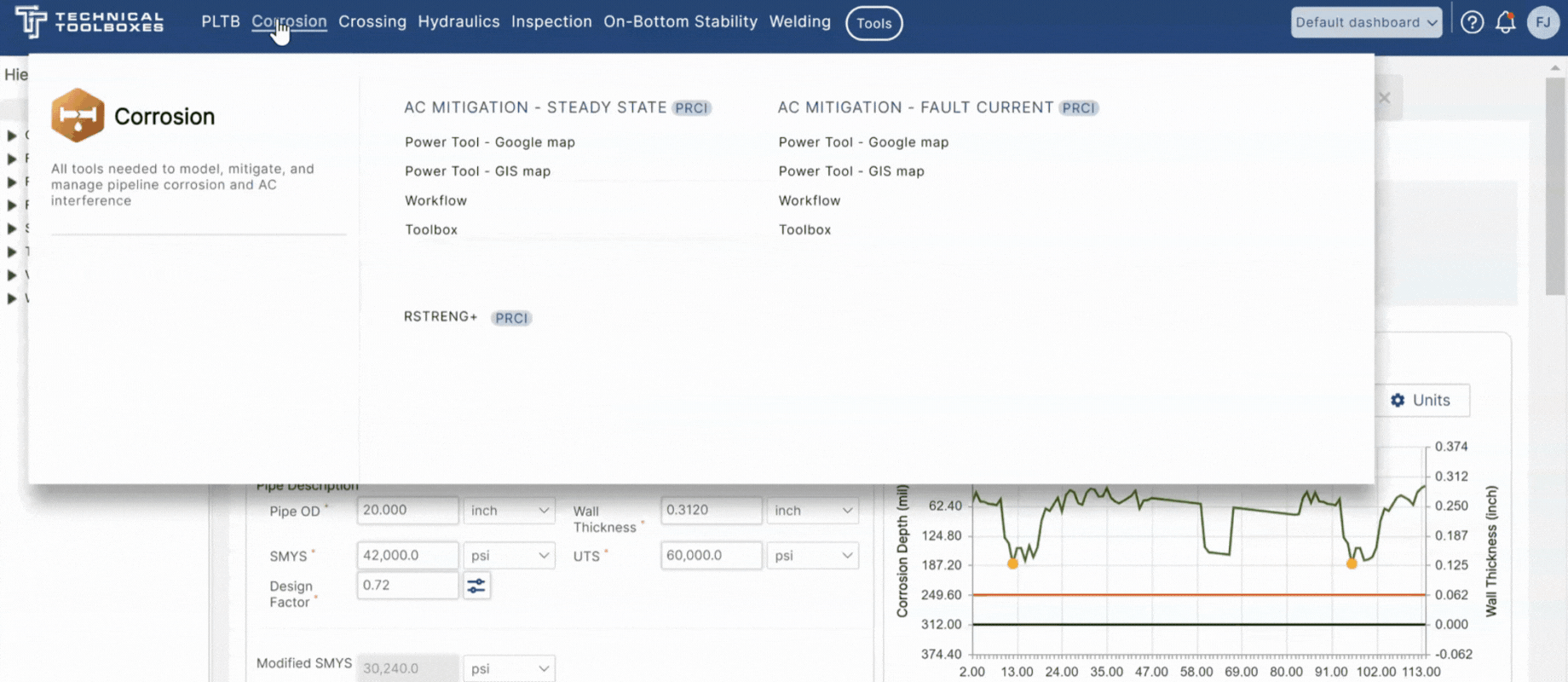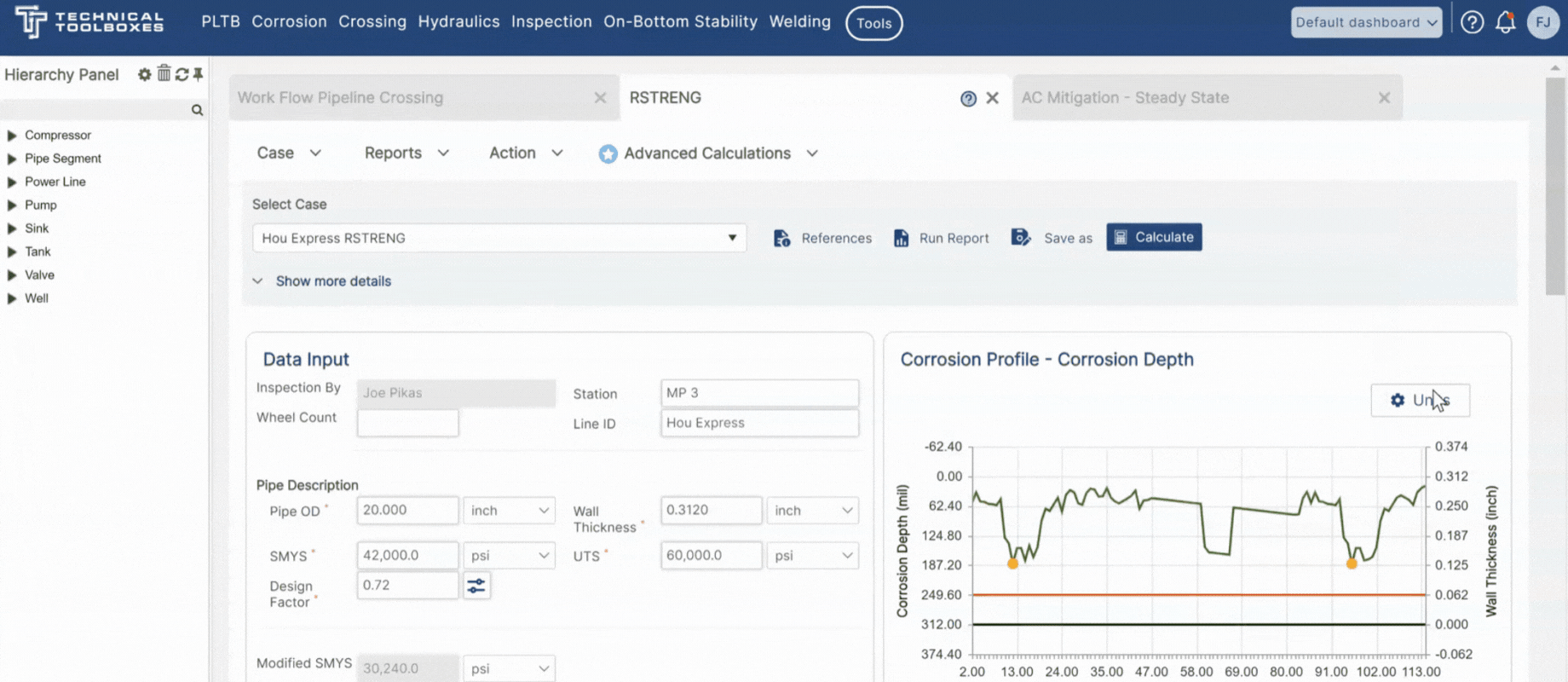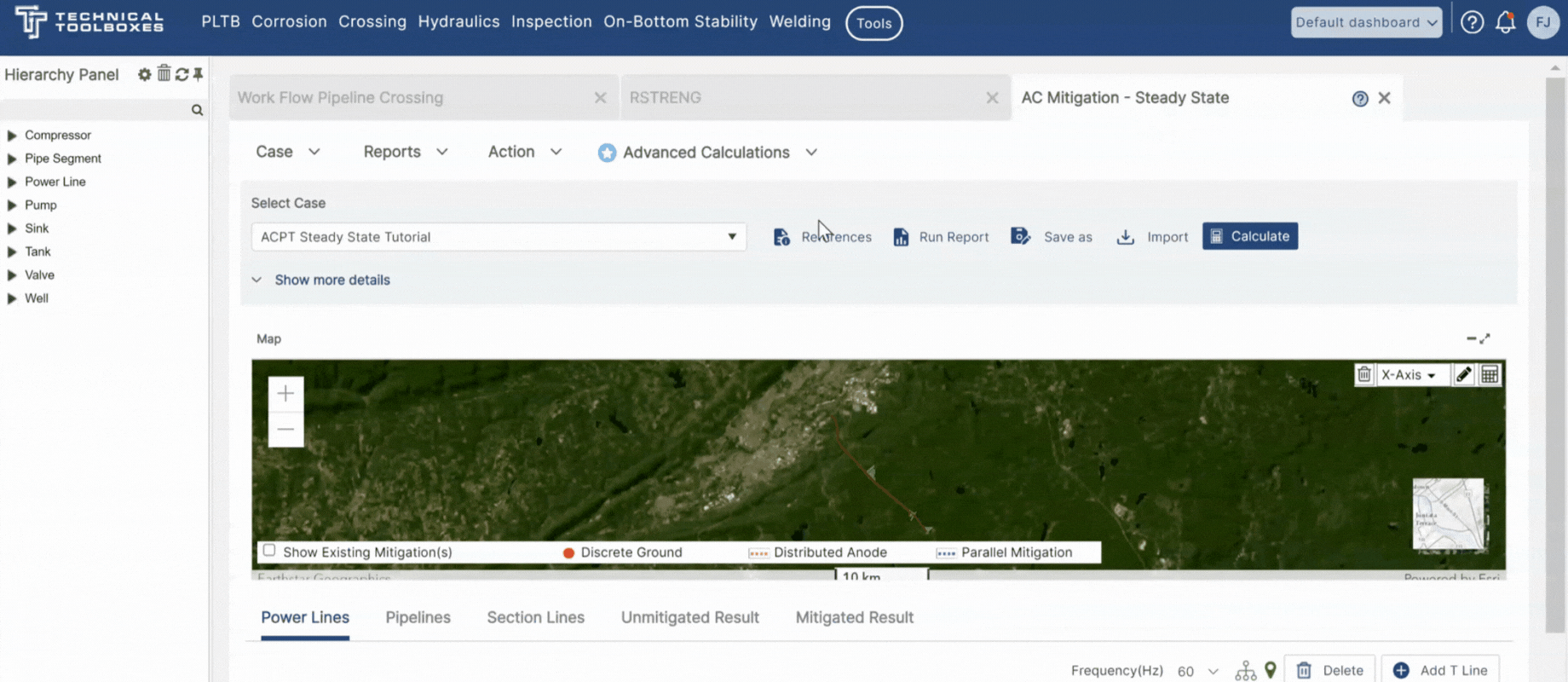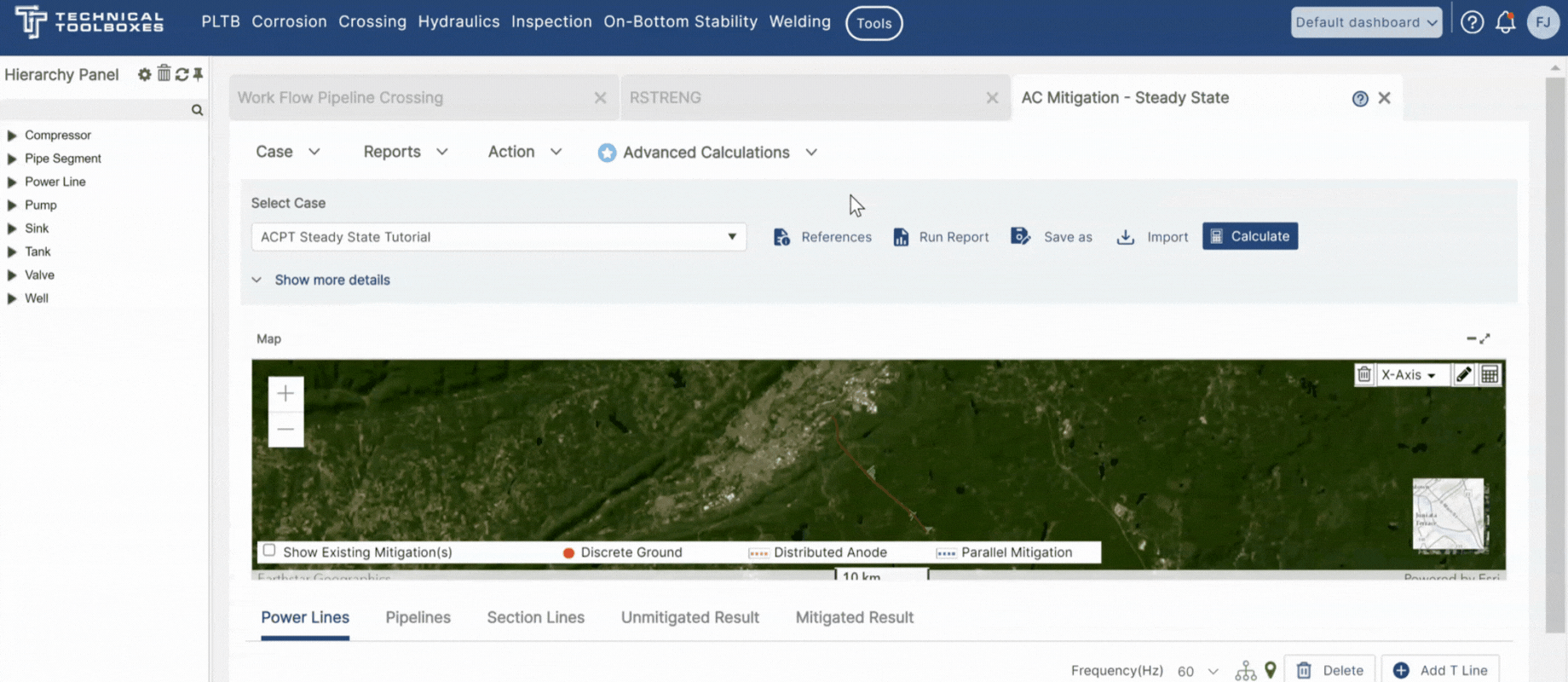
| RSTRENG+ | Determine reassessment intervals Determine remaining life & metal loss Verify & optimize in-line inspection (ILI) |
192.933, 192.485, 192.632, 192.7 |
| AC Mitigation PowerTool | Induced steady State Voltages Fault Currents Mitigation of AC interference Risk reduction Lowers threats & Increase Safety Integrates GIS mapping |
192.473 |
| Hydrotest PowerTool | MAOP validation Strength & Integrity checks Leak tests Spike tests |
192.917 |
Watch our previously recorded webinar on “Streamlining PHMSA Mega Rule Compliance Using Software” or attend our training on “Corrosion Management of Aging Pipelines”
Or contact me, the author, Joe Pikas, at [email protected]
Suggested Post
The Network Modeling Tool Gas Engineers Didn’t Know They Needed
The Network Modeling Tool Gas Engineers Didn’t Know They Needed By Kesley Price You’ve outgrown your spreadsheets, now [...]
The Trusted Tool Gas Engineers Didn’t Know They Were Missing
Do You Really Know What’s Flowing Through Your Pipes? The Trusted Tool Gas Engineers [...]
2026 API Compliance: What You Need to Know
2026 API Compliance: What You Need to Know By Kesley Price New rules. Tougher [...]